The development of this first tranche of orbital data center capability (ODC T1) will support the transformation of low-Earth orbit (LEO) into a global space marketplace by maturing the necessary technologies and infrastructure for large-scale and secure space-based data processing. One of the key features of the orbital data center is “Earth independence” – the ability to provide in-space cloud services without the need to connect back to terrestrial cloud infrastructure. ODC T1 will help operationalize data processing and management applications for Axiom Space’s customers, while setting the stage for lunar and Mars use cases where on-premises data processing will be required to support exploration and economic development beyond Earth’s orbit.
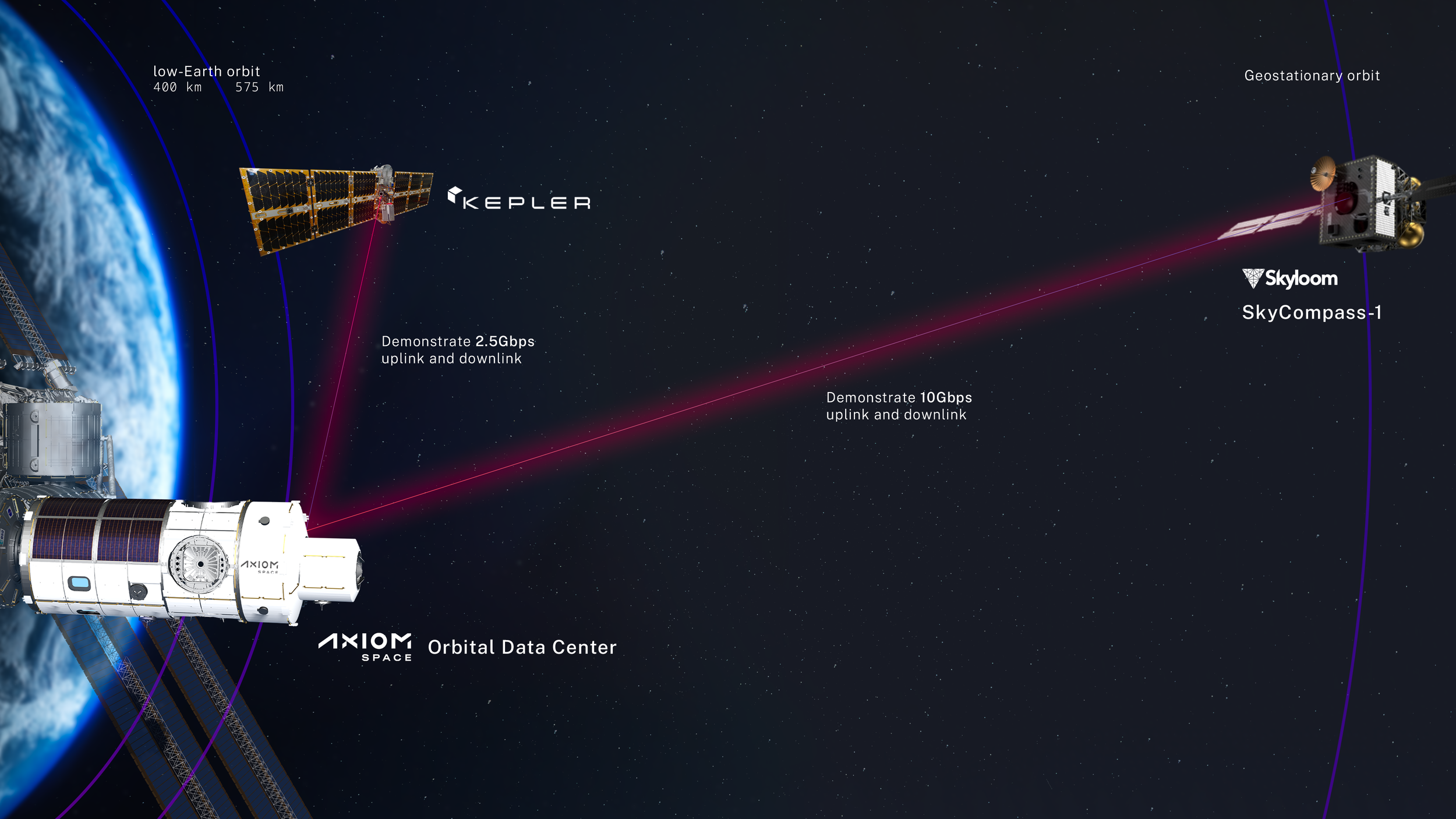
The effort with Kepler and Skyloom will enable demonstration of OISLs to allow for data to be transmitted to and from the orbital data center via the Kepler and Skyloom relay constellations. The OISLs will allow for up to 10 gigabits-per-second data throughput and meet Space Development Agency (SDA) interoperability standards.
“This is a pivotal moment for in-space data processing infrastructure and capabilities,” said Jason Aspiotis, Axiom Space’s Director of In-Space Infrastructure & Logistics. “For the past two years, our team has been demonstrating proof of concepts and developing use cases for in-space data processing infrastructure. The ODC T1 effort and collaboration with Kepler and Skyloom will help us realize our vision of building and operationalizing the world’s first orbital data center. The data center will provide unprecedented data storage and processing capacity in a commercial, scalable, and economical way to aid microgravity researchers, Axiom Station users, and satellites in LEO, medium-Earth orbit (MEO) and Geosynchronous Equatorial Orbit (GEO) through optical communications relays and via the extended mesh network.”
In preparation for the ODC T1 deployment, Axiom Space plans to install a smaller data processing prototype aboard the International Space Station to conduct testing and demonstrate initial capabilities. The prototype is planned for launch in 2024 and will test applications in artificial intelligence and machine learning, data fusion, and space cybersecurity.
“We will work to validate use cases at a sub scale and, at the same time, obtain flight heritage on the underlying data center hardware,” said Aspiotis. “Having a prototype on the ISS will serve as a building block toward the roughly half-cubic-meter sized data server rack we plan to launch by 2027.”
Axiom Space is also actively conducting demonstrations on the AWS Snowcone currently aboard the space station, proving the basic utility of a data center in space and implementing processes and procedures for future orbital data center operations.
“Kepler’s SDA-compatible space relay network leverages the latest technological advances in optical communications,” said Steve Bennett, Chief Operating Officer for Kepler. “We are pleased to partner with Axiom Space to provide 24-7 on-orbit capabilities to demonstrate the benefits our low latency, high-throughput data relay network can provide Axiom Space’s orbital data center. With the proliferation of spacecraft in LEO, the demand for continuous, high-capacity connectivity on orbit continues to grow. The Kepler Network is designed to help close the business case for commercial space stations, Earth observation companies, and other space operators requiring low latency and high bandwidth connectivity.”
“Skyloom is excited to partner with Axiom Space,” said Eric Moltzau, Skyloom’s Chief Commercial Officer. “This demonstration will prove the competitive advantages of our SkyCompass-1 optical communications network, which we are jointly developing and deploying with Space Compass and which will offer services beginning in 2025. This project with Axiom Space will illustrate SkyCompass-1's low latency, high bandwidth network capabilities.
“Skyloom is a network service provider and space-based telecom equipment manufacturer,” Moltzau added. “We build all the infrastructure to support network services and we see the partnership with Axiom Space as a tremendous opportunity to grow together to provide these services for all kinds of commercial and government users. This demonstration is the start of laying the initial infrastructure for a Commercial Space Internet to flourish in near earth orbit and on a planetary scale.”
Once Axiom Station Hab One (AxH1) is connected to the ISS, the data center hardware and optical communications terminals will be flown to AxH1 for module integration in preparation for initial testing. ODC T1 is planned to launch by 2027. The testing expects to prove out an array of capabilities, including 24/7 and high-bandwidth data connectivity between Axiom Station via a LEO and GEO relay network back to Earth; real-time voice and video capabilities for Axiom Station and its crew; high-speed data transport from experiments and payloads; connectivity and interoperability between LEO and GEO satellites with AxH1 as a network translation node; and orbital data center use cases in Earth-independent data storage and fusion, artificial intelligence and machine learning, and in-space cybersecurity. Once testing and evaluation are complete, the ODC T1 will be ready for real-time operations on orbit in support of Axiom Station customers and the mesh network.
The commercialization of LEO promises to stimulate new markets, drive innovations and fuel new ideas to advance civilization. The development of space-based data centers, equipped with cloud technology and advanced cyber security, is an integral part of creating a sustainable communications ecosystem capable of supporting human spaceflight, exploration, and commerce in space to generate economic and social value for the world.
About Kepler
Kepler Communications US Inc. is a satellite telecommunications provider on a mission to build the Internet for space. Incorporated in 2015, Kepler provides real-time, continuous connectivity for space communications, abolishing barriers to make space-generated data universally available. The Kepler Network will initially service low earth orbit (LEO) and plans to provide connectivity services to space missions in LEO, MEO, GEO, and beyond. Kepler is building a global company to enable communications for the future space economy. To learn more about Kepler Communications US Inc., visit www.kepler.space.
About Skyloom
Skyloom is a Broomfield, CO-based telecommunications innovator founded with the mission to develop, deploy, and operate one of the fundamental pieces of tomorrow's space-based telecommunication infrastructure for the provision of data transport services on a planetary scale. They leverage deep heritage in space optical communications to enable real time data transfer so that customers and decision makers can leverage perishable information. www.skyloom.co
About Axiom Space
Axiom Space is building for beyond, guided by the vision of a thriving home in space that benefits every human, everywhere. The leading provider of human spaceflight services and developer of human-rated space infrastructure, Axiom Space operates end-to-end missions to the International Space Station today while developing its successor, Axiom Station – the world’s first commercial space station in low-Earth orbit, which will sustain human growth off the planet and bring untold benefits back home. For more information about Axiom Space, visit www.axiomspace.com.